Cloud Server Infrastructure – As businesses increasingly rely on digital technologies, the demand for scalable, flexible, and reliable IT infrastructure has never been higher. Cloud server infrastructure has emerged as a game-changer, providing organizations with the tools and resources to innovate, scale, and optimize their operations. Cloud computing allows businesses to host applications, store data, and run services in a highly efficient, cost-effective, and secure environment.
This article explores the concept of cloud server infrastructure, its components, how it works, its benefits, and how organizations can leverage it for success in the digital age.
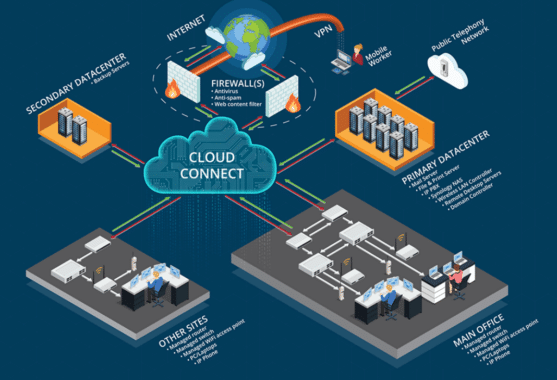
What is Cloud Server Infrastructure?
Cloud server infrastructure collects hardware and software resources required to deliver cloud computing services. Unlike traditional on-premises IT infrastructures, cloud server infrastructure is hosted off-site and is typically managed by third-party cloud providers. These providers offer computing power, storage, networking, and other services on a pay-as-you-go basis, allowing businesses to access computing resources without investing heavily in physical hardware or data centres.
Cloud server infrastructure includes the following key elements:
- Virtualized Servers: These virtual machines (VMs) run on physical servers in a data centre. The virtualized nature of cloud servers allows businesses to scale their resources dynamically.
- Storage: Cloud storage solutions store and manage data, offering both object- and block-based storage options.
- Networking: Cloud networking allows cloud servers to communicate with one another and external systems, enabling data transfer, communication, and remote access.
- Management Tools: Cloud server infrastructure includes monitoring and management tools to optimize performance, manage workloads, and ensure security and compliance.
Key Components of Cloud Server Infrastructure
Cloud server infrastructure comprises several interdependent components that provide businesses and individuals with a reliable and scalable environment. Some of the most critical components include:
- Compute Resources
Compute resources are the core of cloud infrastructure. They represent the processing power needed to run applications, websites, and services. Cloud servers, typically virtual machines (VMs), are allocated from a pool of physical servers in the cloud provider’s data centre. The ability to provision computing resources on demand is one of the key advantages of cloud infrastructure, as it allows businesses to scale their operations efficiently based on their needs.
- Storage Solutions
Cloud storage allows data to be stored off-site, removing the need for physical storage devices. Cloud storage is scalable, meaning businesses can adjust the amount of storage they need without purchasing additional hardware. Common types of cloud storage include block storage (for data that requires fast access), object storage (for storing large amounts of unstructured data), and file storage (for sharing and accessing files across teams).
- Networking
Cloud networking connects virtual servers, data centres, and users to facilitate data exchange. It enables services like load balancing, VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), and direct connections to external networks. Cloud networking ensures data can be transferred between cloud resources efficiently and securely. Advanced networking capabilities, such as content delivery networks (CDNs), are often included in cloud server infrastructure to improve speed and performance.
- Virtualization
Virtualization creates virtual versions of physical resources, such as servers, storage, and networks. Through virtualization, cloud providers can optimize the use of physical hardware, ensuring maximum resource utilization. Virtualization enables businesses to run multiple applications and services on a single physical server by creating multiple virtual instances. This maximizes efficiency and scalability.
- Automation and Orchestration
Automation refers to using tools and processes that automate cloud resource provisioning, scaling, and management. This allows businesses to streamline their operations and ensure that resources are always available when needed. Orchestration involves coordinating multiple automated processes to manage workflows in various cloud environments. Automation and orchestration improve efficiency, reduce human error, and enhance scalability.
- Security
Cloud server infrastructure relies heavily on strong security measures to protect data and resources. These include encryption (at rest and in transit), access controls, firewalls, multi-factor authentication, and intrusion detection systems. Ensuring cloud infrastructure security is critical to maintaining data privacy and compliance with industry regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA.
- Monitoring and Management Tools
Monitoring tools track the performance and health of cloud servers and infrastructure. These tools provide visibility into computing, storage, and network resource usage. They also enable businesses to monitor applications and services for downtime, performance degradation, and security vulnerabilities. Standard monitoring tools include Amazon CloudWatch, Microsoft Azure Monitor, and Google Cloud Operations Suite.
Types of Cloud Server Infrastructure
Cloud server infrastructure can be deployed in several different ways to meet the specific needs of businesses. The most common types of cloud infrastructure include:
- Public Cloud
- In a public cloud model, cloud resources are owned and managed by third-party providers and are shared among multiple customers. This type of infrastructure is ideal for businesses looking to minimize their upfront investment in hardware and data centres. Public cloud providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, offer various services, including computing, storage, and networking.
- Advantages: Cost-effective, scalable, and no need to manage physical hardware.
- Disadvantages: Shared resources may raise security or privacy concerns for some organizations.
- Private Cloud
- A private cloud is a cloud infrastructure dedicated to a single organization. This infrastructure can either be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. Private clouds offer businesses greater control over their resources and are often used by organizations with specific security, compliance, or performance requirements.
- Advantages: Enhanced security, more control, and custom configurations.
- Disadvantages: More expensive than public clouds due to dedicated resources.
- Hybrid Cloud
- A hybrid cloud combines elements of both public and private clouds, allowing organizations to use both on-premises and cloud-based resources. Hybrid clouds offer flexibility by enabling businesses to move workloads between private and public clouds. This model is ideal for companies that require the scalability of the public cloud but also need the security of a private cloud for specific workloads.
- Advantages: Flexibility, cost-efficiency, and security.
- Disadvantages: Complexity in management and integration.
- Multi-cloud
- A multi-cloud strategy involves using services from multiple cloud providers. This approach allows businesses to take advantage of the unique strengths of each cloud provider while minimizing the risk of vendor lock-in. Enterprises with complex needs requiring diverse cloud services and capabilities often use multi-cloud environments.
- Advantages: Redundancy, reduced reliance on a single provider, and flexibility.
- Disadvantages: Increased complexity and potential challenges in integration and management.
Benefits of Cloud Server Infrastructure
Adopting cloud server infrastructure offers numerous benefits to organizations of all sizes. Some of the key advantages include:
- Scalability
One of the most significant benefits of cloud server infrastructure is its scalability. Cloud resources can be easily scaled up or down based on demand. This elasticity enables businesses to only pay for the resources they use rather than over-provisioning hardware and infrastructure.
- Cost-Efficiency
Cloud server infrastructure eliminates the need for significant upfront investments in physical hardware. Businesses can instead pay for cloud resources on a subscription or pay-as-you-go basis. This flexibility reduces capital expenses and helps organizations optimize their IT budgets.
- Reliability and Uptime
Leading cloud providers offer high uptime guarantees (typically 99.9% or more) and provide built-in redundancy and failover capabilities to ensure high availability. This reliability is essential for businesses that rely on constant uptime for their operations.
- Flexibility
Cloud server infrastructure allows businesses to access various applications and services, from hosting websites and databases to running machine learning models and big data analytics. Cloud environments are also agnostic in operating systems, meaning businesses can run various software stacks.
- Security
Cloud providers offer robust security features, including data encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection. They also provide compliance with industry standards and regulations, making cloud server infrastructure a secure choice for businesses that need to protect sensitive data.
- Global Accessibility
Cloud server infrastructure is typically distributed across multiple data centres in different regions. This global presence ensures that businesses can provide low-latency access to their services and data, regardless of their users’ location.
Conclusion
Cloud server infrastructure has become the backbone of modern IT, allowing businesses to scale, innovate, and optimize operations in a cost-effective and secure environment. By leveraging cloud server infrastructure, organizations can access computing, storage, and networking resources on-demand without requiring extensive physical hardware investments. As cloud technologies evolve, businesses adopting cloud infrastructure will be well-positioned to stay competitive in an increasingly digital world.

